Table of Contents
How to start the stack
Start simulation as described in LGSVL simulator. Additionally, to configure LGSVL for this demonstration:
- Maps: use this map link
- Vehicles: Select
ROS2 nativebridge type and paste the content ofAutowareAuto/lgsvl-sensors.jsoninto theSensorstext box - Simulations: In
Generaltab,Select Cluster = Local Machineand untick any boxes. InMap & Vehiclestab, ensure to untickRun simulation in interactive mode. InTraffictab, untick all selection. TheWeathertab is irrelevant.
terminal 1
terminal 2
The stdbuf command above is needed because the default in ROS is to only output lines from stdout when the buffer is full. This command changes that setting to use a "line buffer" which outputs every line, providing more debugging information.
terminal 3
Move the vehicle on LGSVL to the position shown in the image. This is the "pick-up/drop-off zone" on the parking lot roadway in front of the three parking spots directly outside of the front door of the AutonomouStuff building.
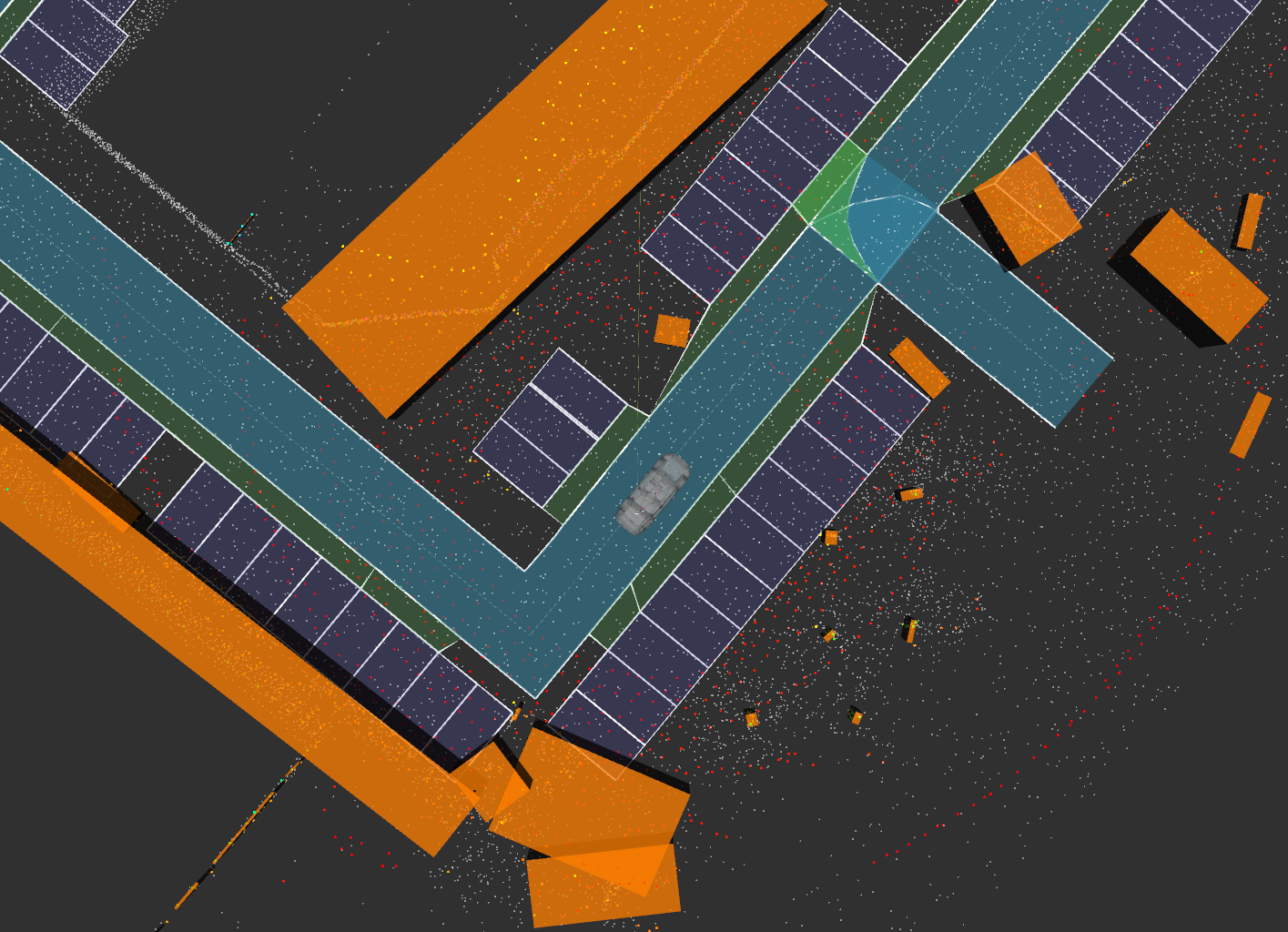
Before selecting a goal, you will need to initialize localization. To do this switch to the rviz window, click the 2D Pose Estimate button at the top, and then click at the approximate location where the vehicle currently is in the map and drag in the direction of the vehicle's heading. You can verify that the vehicle has been localized by the vehicle model jumping to the new location and the real-time lider scans matching up with the static lidar map.
Next, to select a parking spot graphically, click the 2D Nav Goal button in rviz, click in the goal location, and drag in the direction of the goal heading.
Optionally, to send a goal position/heading programmatically:
terminal 4
The path with lane IDs should be output in terminal 3.
Note To choose a different parking spot, click 2D Nav Goal in rviz and listen to the message with
ros2 topic echo /goal_pose
and update the values in the message in YAML format above.
Passing metrics
The output message looks like
To check if the route is reasonable, open the OSM map AutowareAuto/src/tools/autoware_auto_avp_demo/data/autonomousstuff_parking_lot.osm in a text editor and search for way id='9824. It references a node, the center of the entrance line, 9831 in this case. Searching for its coordinates, they are:
To graphically inspect this, install the qgis tool with:
and follow this tutorial to open the .osm file. Finally, install a plugin called Lat Lon Tools and enter the coordinates to pinpoint the node with a red crosshair.